The Crucial Role of Specialty Chemicals in UV Protection and Sunscreens.
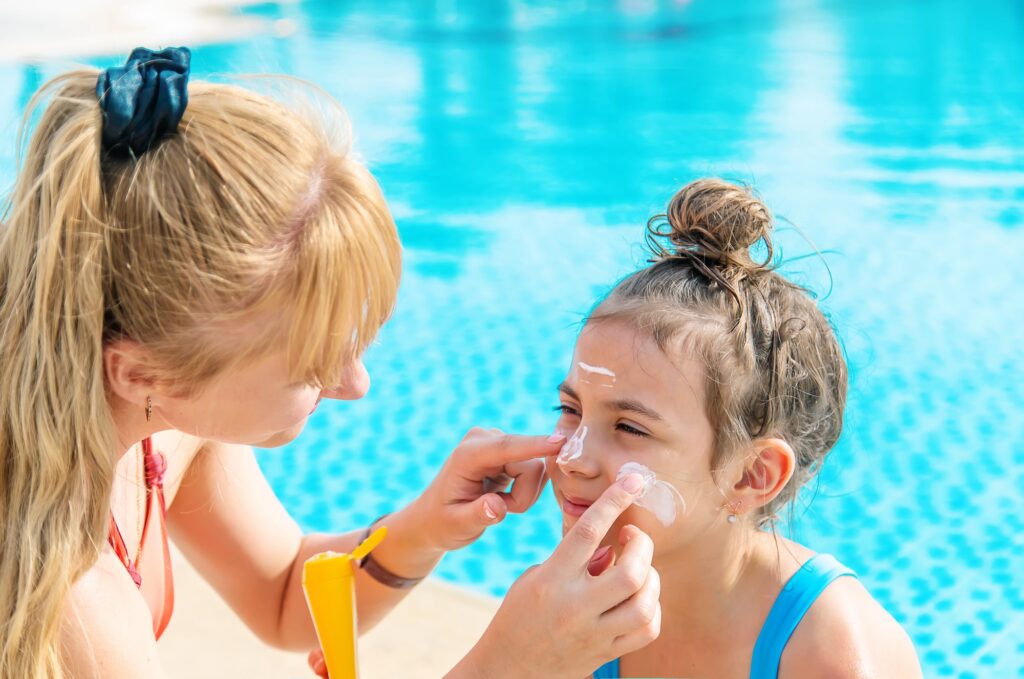

As summer unfolds, concerns about sun protection become increasingly important. The increasing awareness of the dangers associated with UV radiation has driven the demand for effective sunscreens. Specialty chemicals play a critical role in enhancing the efficacy of these products, ensuring they provide robust protection against harmful UV rays. This post explores the science behind UV protection, the effectiveness of different specialty chemicals in sunscreens, and recent advancements in UV protection technology. We will also emphasize the importance of these chemicals in safeguarding public health and safety.
The Science Behind UV Protection
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is divided into three categories based on wavelength: UVA, UVB, and UVC.
- UVA (320-400 nm): Penetrates deep into the skin, causing premature aging and wrinkles, and can also contribute to skin cancer.
- UVB (280-320 nm): Affects the outer layer of the skin, causing sunburn and playing a significant role in the development of skin cancer.
- UVC (100-280 nm): Absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere and does not reach the surface.
Sunscreens are formulated to protect the skin by absorbing, reflecting, or scattering UV radiation. The effectiveness of a sunscreen is indicated by its Sun Protection Factor (SPF), which measures its ability to protect against UVB rays. Broad-spectrum sunscreens offer protection against both UVA and UVB radiation.
Specialty Chemicals in Sunscreens
The active ingredients in sunscreens are either organic (chemical) filters or inorganic (physical) filters. Each type of filter has distinct properties that contribute to UV protection.
Organic Filters: Organic filters, also known as chemical filters, absorb UV radiation and convert it into heat, which is then released from the skin. Some commonly used organic filters include:
- Avobenzone: Provides broad-spectrum protection by absorbing UVA rays. It is often combined with other filters to enhance stability and effectiveness.
- Octocrylene: Absorbs UVB and short UVA rays. It also stabilizes other sunscreen ingredients like avobenzone.
- Oxybenzone: Offers broad-spectrum protection but has raised concerns regarding its environmental impact and potential health risks.
Inorganic Filters: Inorganic filters, also known as physical filters, reflect and scatter UV radiation. The most common inorganic filters are:
- Titanium Dioxide: Provides broad-spectrum protection, primarily against UVB and short UVA rays. It is known for its safety and stability.
- Zinc Oxide: Offers comprehensive protection against both UVA and UVB rays. Zinc oxide is non-irritating and suitable for sensitive skin.
Effectiveness of Specialty Chemicals in Sunscreens
The effectiveness of sunscreens depends on the combination and concentration of active ingredients. Specialty chemicals enhance the performance of these ingredients, ensuring optimal protection and user experience.
Stabilizers and Photostabilizers: Some organic filters can degrade when exposed to sunlight, reducing their effectiveness. Photostabilizers are added to sunscreens to enhance the stability of these filters. For example, octocrylene not only acts as a UV filter but also stabilizes other ingredients like avobenzone.
Encapsulation Technologies: Encapsulation of UV filters within liposomes or nanoparticles can improve their distribution on the skin and enhance their stability. Encapsulated filters provide a more even coverage, reducing the likelihood of gaps in protection.
Antioxidants: UV radiation generates free radicals that can damage skin cells. Antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, are added to sunscreens to neutralize these free radicals, providing additional protection and supporting skin health.
Emulsifiers and Emollients: These ingredients improve the texture and spreadability of sunscreens, ensuring even application. They also enhance the water-resistance and durability of the product, making it more effective during outdoor activities.
Recent Advancements in UV Protection Technology
The field of UV protection is continuously evolving, with ongoing research and innovation leading to the development of more effective and user-friendly sunscreens.
Nanotechnology: Nano-sized particles of titanium dioxide and zinc oxide offer superior protection while minimizing the whitening effect, providing a transparent finish.
Broad-Spectrum Protection: New filters like Tinosorb S and Tinosorb M offer high photostability and broad-spectrum protection.
Environmental Considerations: Development of reef-safe sunscreens using alternative UV filters that are less harmful to marine life, such as non-nano zinc oxide.
Smart Sunscreens: Sunscreens that increase their SPF when exposed to higher UV levels and those integrating UV sensors to alert users when to reapply.
DNA Repair Enzymes: Incorporation of DNA repair enzymes in sunscreens helps repair UV-induced DNA damage, offering an extra layer of protection.
The Importance of Specialty Chemicals in Public Health and Safety
Specialty chemicals in sunscreens play a crucial role in public health and safety by providing effective protection against harmful UV radiation. Prolonged exposure to UV rays can lead to serious health issues, including skin cancer, premature aging, and eye damage. Sunscreens are an essential tool in reducing these risks.
Skin Cancer Prevention: Skin cancer is one of the most common cancers worldwide. Regular use of sunscreen significantly reduces the risk of developing skin cancer by protecting against the harmful effects of UV radiation. Broad-spectrum sunscreens, containing both UVA and UVB filters, are particularly effective in preventing skin cancer.
Anti-Aging Benefits: UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin and contribute to the breakdown of collagen and elastin, leading to wrinkles and sagging. By protecting against UVA radiation, sunscreens help maintain skin’s youthful appearance and prevent premature aging.
Protection for Vulnerable Populations: Certain populations, such as children, individuals with fair skin, and those with a history of skin cancer, are more susceptible to UV damage. Sunscreens formulated with gentle and effective specialty chemicals, like zinc oxide, provide essential protection for these vulnerable groups.
Supporting Overall Skin Health: In addition to preventing sunburn and skin cancer, sunscreens with added antioxidants and moisturizers support overall skin health. They protect against the oxidative stress caused by UV radiation and help maintain the skin’s barrier function.
In conclusion, as we gear up for the summer season, the importance of effective sun protection cannot be overstated. Specialty chemicals in sunscreens are at the forefront of this effort, providing robust and reliable protection against harmful UV rays. Through advancements in formulation technology and a focus on environmental sustainability, the coatings and paints industry continues to innovate, ensuring that consumers have access to high-quality, effective sunscreens.
The role of specialty chemicals in enhancing the performance and safety of sunscreens underscores their significance in public health. By understanding the science behind UV protection and staying informed about recent advancements, consumers can make informed choices that protect their skin and overall health. As we enjoy the sunny days ahead, let us not forget the critical role that specialty chemicals play in keeping us safe from the sun’s harmful rays.